600 Volt Wire and Beyond: Some Common Abbreviations and What They Mean
1st Feb 2022
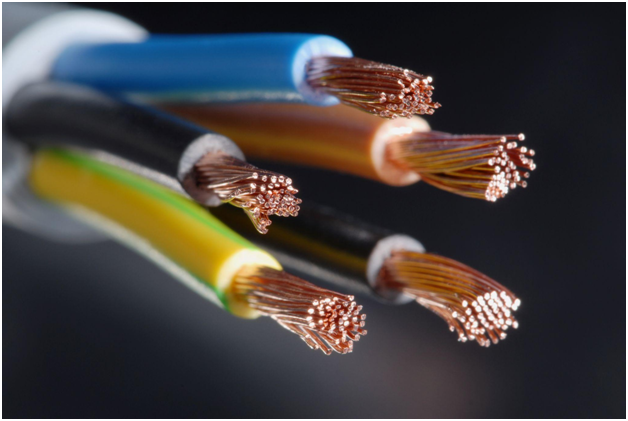
For many building applications, 600-volt wire is a standard. There are wires rated to 600 volts that can be used for a wide range of applications.
That said, while there is a decent amount of variability in gauge size and conductor quality, such as the fineness of the conductors, the material from which they are made, or how they are treated, there is much more variability in their jacketing.
Jacketing, or insulation, protects electrical wire and cable from the elements and renders them suitable - or not so suitable - for a given environment. Not all wires are 600-volt wire, and not all wires have the same insulation.
These are some common abbreviations you might see stamped on electrical insulation, and what they mean - some are far more common than others.
● B - Braid insulation, typically made of fiberglass. It is highly flexible and resistant to moisture and chemicals. A special type is known as MG, which has fiberglass outer and mica inner insulation.
●DBRC - Double braided, rubber, with cotton insulation. This type is rarely found nowadays, but was once commonly used because it was resistant to fire as well as the elements.
●E - E typically denotes elevator cable, which commonly has layers of cotton braiding along with flexible, moisture resistant, flame retardant nylon jacketing as well.
●FCC - FCC denotes flat copper conductors, which are commonly used under flooring or carpeting.
●FEP - Useful only in dry settings, FEP stands for fluorinated ethylene propylene, which is soft, resistant to sunlight and some chemicals.
●HH - HH in wiring connotes high heat resistance. Often this designator is paired with other traits. Wires given an “HH” designation are often used in settings where high temperatures are the norm and thermal stress should be expected.
●L - Lead jacket; not particularly common, but lead was once commonly used as an insulator earlier in the 1900s. Because it is soft and insulates the cables it was considered effective but has fallen out of favor to much safer, more resistant polymer alternatives.
●MI - Mineral insulated; these cables can be used in both wet or dry locations.
●MTW - Machine tool wiring, typically made with a nylon outer jacket. It is moisture, heat, oil-resistant, and flame retardant.
●N - Nylon, typically extruded nylon. It is very flexible and durable, as well as resistant to oil, gas, and some chemicals.
●NM - Non-metallic cable insulation, typically protected with plastic sheeting and paper wrappings between the conductors.
●PF - Similar to fluorinated ethylene propylene, typically used as fixture wire and can be single-stranded or braided (wire or cable, respectively).
●PFA - Perfluorglkoxy, sometimes also referred to as PAF. Similar to PTFE insulation, PFA is chemical and oil resistant as well as resistant to high temperatures. It is also very flexible and can be used in dry or damp (not wet) environments.
●R - Rubber; sometimes used for household wiring as rubber is well-respected for its non-conductive properties.
●RFH-1 - Rubber coated and heat resistant; more durable and temperature resistant than R.
●SA - Silicone asbestos (or rubber), can be used in both dry and damp locations. Sometimes it also features additional braided insulation for better protection.
●SE - Service entrance wire, very durable, typically has a tough thermoplastic sheathing or additional insulation. Usually, flame and moisture resistant and may be rated for underground use.
●SJT - A special type of service cord that features thermoplastic insulation.
●T - Connotes thermoplastic insulation, typically most suitable for use at cooler temperatures. May refer to tinsel cord.
●TW - Thermoplastic, water-resistant; may be suitable for use in both wet and dry locations. Resistant to water, heat, and sometimes fire.
●TFE - Polytetrafluoroethylene, extended; only suitable for use in dry locations. May be used for approved raceways.
●TFN - Thermoplastic, heat resistant, nylon jacket.
●THW - Heat resistant, flame retardant, may be suitable for use in both wet and dry locations.
●THHN - Thermoplastic, high heat resistant, nylon insulation; better conductor temperature protection. Also may be flame retardant and suitable for dry and damp locations.
●THHW - Thermoplastic, high heat resistant, but suitable for use in wet locations.
●THWN - Thermoplastic, heat and water-resistant, with a nylon jacket.
●TPE - Thermoplastic elastomer; similar to PVC, flexible, highly resistant to cold, and much lighter than rubber.
●X - Connotes a cross-linked polymer, like XLPE (cross-linked polyethylene). Cross-linked polymers are extremely tough and resistant to both heat and moisture.
●XF - Cross-linked polyolefin, this material is highly UV-resistant.
●XHHW - Cross-linked polymer, high-heat resistant, water-resistant.
●Z - Modified ethylene tetrafluoroethylene, which is durable, corrosion-resistant, and resistant to heat, temperature, chemicals, and certain types of radiation.
Interested in learning more about the different types of 600-volt wires and other specialized residential, commercial and industrial wires and cables that you can find here on our site or might find out in the field? Give us a call at 800-262-1598 and we’d be glad to help.
General purposes wiring like 600-volt wire is not always the most suitable choice for a location. Depending on the unique circumstances surrounding the environment or the needs of the circuit, a higher or lower voltage rating may be necessary, as may be specific insulation or armor.
Get in touch with us to learn more!

